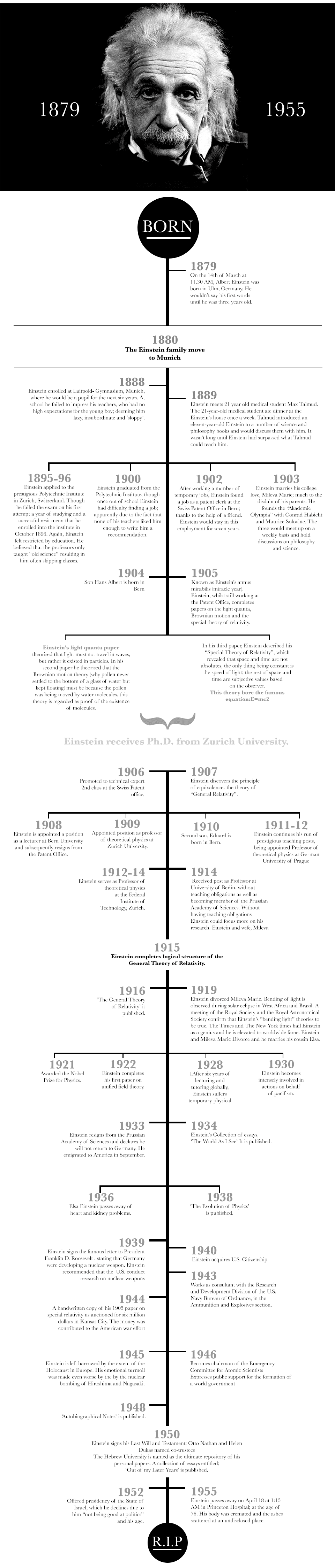
For many people, Albert Einstein is regarded as one of the smartest people who have ever lived. His theories and postulations continue to live on today and form the basis of many of the theories and laws of space, time, and physics that we use for our modern inventions. Einstein goes beyond the typical equation of E=MC2 with these fantastic inventions. Let’s take a look.
#1. Tracking Brownian Motion
In physics, Brownian Motion is how particles move within a fluid. Up until Einstein, there was no real way to measure or track this movement, even though it was known that the particles did move. What he did was develop the mathematical model that could accurately show this movement, although it was initially criticized for being incorrect until Einstein proved it through experimentation.
#2. Theory of Relativity
This is where the E=MC2 equation comes into play. This is his most well-known invention and it has been the foundation of many of today’s modern inventions, including the unfortunate development of the nuclear bomb. It has also provided us with abundant energy thanks to it being the foundation of nuclear power as well. What does this theory say? In short, it basically means that the laws of nature are fundamentally the same throughout the entire universe and that the speed of light always remains constant.
#3. Photons
Less of an invention and more of a discovery, Einstein had thought as early as 1905 that lights were actually made up of particles. He called these particles photons and this was eventually proven in 1919 to be accurate. The discovery actually led to Einstein winning the Nobel Prize in 1921 and has become the foundation of much scientific advancement in the use of light.
#4. Einstein Refrigerator
This is really the only traditional invention that Einstein created over the course of his life. Many refrigerators of his day, and even still today, are cooled with Freon. With this invention, the same cooling effect could be achieved with the combination of butane, ammonia, and water. Although the invention never really took off, it is being looked at again today because it takes very little energy to achieve a similar cooling effect.
#5. Quantum Theory of Light
After thinking about light being particles, Einstein also thought that light would be able to travel as protons in waves. This is the photoelectric effect, which means solid objects will emit electrons when they are struck by light. If you have ever watched TV at some point in your life, then you’ll have been able to see Einstein’s theories working practically for you.
#6. Mass and Energy Are Linked
Einstein was also able to prove that his E=MC2 theory could also link mass and energy. It shows that even small particles have an enormous amount of energy, which was contrary to previous scientific thought that related the size of an object to the energy of an object.
Strong proponent of individual liberty and free speech. My goal is to present information that expands our awareness of crucial issues and exposes the manufactured illusion of freedom that we are sold in America. Question everything because nothing is what it seems.